Position Paper 1
Direction for the Ethical Expansion of the Cannabis Industry in Japan
Position Paper 2
MAJIC position on “high compounds”
Position Paper 3
CBD Product Labeling Requirements in Japan
Public Comment Response for THC Levels
MAJIC Advocates for Consumer Safety and the Healthy Growth of the Industry with a 300ppm Δ9-THC Limit for All CBD Products in Japan
Ensuring Fair Standards for THC Testing and Cannabis
Derived Products in Japan
Position Paper 7
On CBN (Cannabinol): Promoting Responsible Use in Japan and Industry-Led Voluntary Governance
MAJIC Position Paper Nr. 1
Direction for the Ethical Expansion of the Cannabis Industry in Japan
Feb 1, 2022
The cannabis industry has seen dramatic growth around the world in the last decade. While there are some areas of growth in Japan, the country has not yet made a concerted effort to wholly participate in the redevelopment of its historically important industry.
The cannabis industry once again offers Japan a unique opportunity to build a viable environment for farmers, entrepreneurs, manufacturers and foreign investors to thrive. The Industry is currently 2021 USD 28.266b and forecasted to grow to USD 197.74b by 2028[1]. As the cannabis industry is revived in Japan, there are many areas that require further clarification, guidance and self regulation. MAJIC (Manufacturers Association of Japan Industrial Cannabis) is dedicated to the ethical and sustainable growth of the cannabis industry in Japan and to promoting constructive dialogue and accurate information.
The following paragraphs identify some of the benefits of cannabis, open questions that require guidance as well as a clear direction from MAJIC for the successful future of the cannabis industry in Japan.
The cannabis plant offers a wide variety of applications in nutrition, health foods, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, sustainable building materials, clothing, fuels, plastics and a growing number of industries. It is one of the most versatile and sustainable plants on the planet with an ability to grow almost anywhere. It reaches maturity within 10 to 32 weeks depending on the climate and can be easily grown without the use of fertilizers or harmful chemicals. In short, Cannabis offers a viable ecologically friendly solution for sustainable products across multiple industries.
It has been utilized over many hundreds of years and after a period of general prohibition in the second half of the twentieth century, cannabis is once again being recognized around the world for all of its benefits it has to offer. With the resurgence of interest in cannabis, a significant amount of scientific research has emerged, further confirming the advantages the plant can provide[2].
Several countries have taken the lead in the rebuilding of the cannabis industry through establishment and changes to laws and policies that allow for the large-scale growing, production and commercialization of cannabis. Legalization of the use of over 100 compounds found in cannabis is progressing as nations realize the health, social, economic and environmental benefits. Canada[3], Mexico[4], South Africa[5] and a large proportion of the United States[6] are just a few of the countries leading the growth. Europe is moving in the same direction with Germany recently announcing their plans to fully legalize cannabis[7] . In Asia, Thailand has legalized cannabis[8] and is moving forward as the first country in the region to proactively redevelop their cannabis industry. China has become a major grower of cannabis, while Korea allows it for medical use[9]. Hong Kong[10] and Japan allow the sale of limited substances from the cannabis plant, such as CBD.
Japan has historically been a major producer and consumer of cannabis products until the end of the last world war. In 1930, marijuana was designated as a narcotic under the Narcotics Control Law, making it difficult to grow and use for medicinal purposes.
In 1948 US occupation forces implemented the cannabis control act (source), which still exists today under which cultivation of cannabis is permitted with some restrictions, and the use of cannabis raw materials derived from stems and seeds, as well as the manufacture and sale of products, are allowed.
The use of THC for any purpose is illegal. [11][12]
The current market and potential growth for each of the above applications are as follows:
Ⅰ Medical
Possible medical uses for cannabis include treatment for epilepsy, sleep, pain, inflammation, eating disorders, GI disorders, alleviation of symptoms associated with chemotherapy and more. Recent research indicates that some cannabinoids found in hemp may be effective in preventing coronavirus from entering human cells[13].
$6,822.21 Million in 2020 and is projected to reach $53,883.46 Million by 2030 registering a CAGR of 23.6% from 2021 to 2030.[14]
Ⅱ Food and Beverages
Food, beverage and supplement applications for cannabis include confectionery, flavoured drinks, cereals, wellness and functional foods (such as protein powders,bars and drinks) and also tincture and capsules based supplements. Pet food is also a growing category.
The cannabis food and beverage market size was valued at $427.0 million in 2018 and is estimated to reach $2,632.0 million by 2026, registering a CAGR of 26.6 % from 2019 to 2026[15].
Ⅲ Fibers
Hemp fiber can be used in building materials, textiles, automotive materials, paper, biodegradable plastics , animal bedding and ropes.
USD 4.46 Billion in 2019, is projected to reach USD 43.75 Billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 33% from 2020 to 2027[16].
Ⅳ Cosmetics and Personal care
Cannabis derivatives including hemp oil and cannabinoids are used in skin care and hair care such as shampoos, conditioners, cleansers,toners, creams, hair and body oils.
The global CBD, skincare market size was estimated at USD 234.1 million in 2018 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32.9% over the forecasted period, from 2019 to 2025[17].
Estimates of the cannabis market size for Japan range widely, mostly due to lack of a coordinated effort to gather accurate data. Japan does appear to lead the Asian market for CBD with several companies initially establishing the market around 2015/2016 and many more companies entering the CBD space in 2020-2021. The Japanese government has established clear policies and procedures for the importation of CBD and other legal compounds found in cannabis. The MHLW(Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare) has commissioned a working group which is in the process of presenting their recommendations so appropriate policies and laws around cannabis can be implemented in the near future[18].
MAJIC was established to ethically lead the Japanese cannabis market through accurate information and self regulation. It is our mission to cooperate with the government and the public to grow the cannabis industry in Japan. We aim to offer Japanese consumers accurate information on the many benefits of the cannabis plant and help grow the Japanese cannabis industry into a globally competitive and attractive market. We work with ethical partners in the industry for productive discussions and
assistance in the formulation of policies. MAJIC is fully dedicated to the growth of the overall cannabis industry, not to a specific company or individual.
The following is a list of topics which MAJIC will pursue along with specific positions when applicable. This list is subject to changes as MAJIC members continue to meet to formulate deeper positions on each topic.
Ⅰ Farming of Cannabis
Japan has a long history of cannabis farming. MAJIC supports the efforts of farmers to advance the growth of cannabis farming in Japan. MAJIC believes that this environmentally sustainable material can play a much larger role across many industries in Japan.
Ⅱ Ethical Advancement of CBD and other Minor Cannabinoids
MAJIC supports the ethical advancement of the established and growing CBD industry in Japan. This includes other so-called “minor cannabinoids” like CBN and CBG which offer health and nutritional benefits without causing a “high” or euphoria. The following is a list of the areas related to CBD and other minor cannabinoids where MAJIC will self regulate and propose further guidelines.
- Definition of CBD and minor cannabinoids: Standardization of definitions is required for proper understanding by the public and for appropriate labeling. This includes defining broad spectrum vs. isolate and CBD naturally derived from hemp vs. synthetic CBD produced from yeast and other sources.
- Appropriate and consistent labeling for clear understanding by the consumer.
- Standardization of personal import requirements to be consistent with requirements placed on Japan-based importers and producers.
- Parts of cannabis plant that can be legally used in the production of cannabis products in Japan. Currently, only the stalk and seed can be used, which is different from worldwide standards. A Japanese government working group has suggested that other parts of the plant could be allowed for the production of CBD. MAJIC supports the expansion of parts of cannabis plant that can be used to bring Japan in line with worldwide standards.
- Promotion of benefits based on scientific evidence: Currently, there are no clear guidelines for the promotion and advertising of CBD and minor cannabinoids. MAJIC would like to work together with the Japanese government to define a list of scientifically based benefits that can be communicated in promotional materials for CBD and minor cannabinoids, while avoiding unnecessary or unsubstantiated claims by promoters of cannabis.
- Self regulation of permissible age for vaping (e-cigarette) of CBD: MAJIC believes that vaping age for CBD should be consistent with vaping age for tobacco (currently 20 years old and above).
- Self regulation for permissible age for CBD consumption; MAJIC believes that CBD can provide various benefits for people of all ages, but recommends that people under the legal adult age should receive parental consent before consuming.
- Recently there are variations of cannabinoids being synthesized (i.e Delta 8, HHC, etc.) which can cause a euphoric effect. MAJIC believes these should be identified, researched for their benefits and risks and proper discussions with the Japanese government should be had to determine whether additional regulation is necessary.
Ⅲ Advancement and proper usage of THC
All of the G7 countries with the exception of Japan allow THC in some shape or form. The Japanese MHLW formed a working group that has made suggestions on the legalization of THC for use in pharmaceutical products. MAJIC understands that THC has therapeutic value and will support the regulated legalization of THC in Japan if and when it occurs. MAJIC supports the Japanese government’s current efforts to find the appropriate way to regulate and utilize this effective compound of cannabis which is currently illegal under the Cannabis Control Act in Japan.
Ⅳ Hemp-based Food & Beverages
Hemp offers a plant-based nutritional alternative for protein, healthy fats, carbohydrates and other components that are well tolerated by the body. MAJIC supports the advancement of hemp-based foods and drinks in Japan.
Ⅴ Hemp Fiber
Cannabis provides environmentally sustainable and economically viable materials for construction, plastics, textiles and many other applications. MAJIC supports the advancement of domestic farming, and production as well as the importation of fibers for these applications.
Ⅵ Cannabis research
Cannabis research has increased greatly as more and more benefits of the plant are discovered. MAJIC supports the development of more cannabis research in Japan for the benefit of the population and the advancement of the Industry.
With the above direction, MAJIC welcomes like-minded organizations working in the Japanese cannabis industry to join us for constructive dialogue together with the Japanese government to further develop an ethical, sustainable cannabis industry in Japan.
- https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/cannabis-marijuana-market-100219
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Legality_of_cannabis_by_U.S._jurisdiction
https://www.bangkokpost.com/thailand/general/2230303/ministry-pushes-full-cannabis-legalisation
Medical Cannabis Market Size, Share | Growth Analysis – 2030
Cannabis Beverages – Market Study by Global Industry Analysts, Inc.
Global CBD Skin Care Market Size & Share, 2025 | Industry Report
MAJIC Position Paper Nr.2
Position of the Cannabis Industry Association of Japan (MAJIC) on “high compounds” (i.e., synthetic cannabinoids intended to produce an intoxicating “high”) such as synthetic HHC and THC-O
May 24, 2022
Recently, many companies have been importing and selling synthetic cannabinoids (so-called “high compounds”) that are intended to produce an intoxicating “high.
Synthetic HHC (hexahydrocannabinoids) were introduced by some Japanese companies in late 2021, and Japanese government authorities moved quickly to make possession and use of HHC illegal. Recently, it has been replaced by THC-O (THC-O-Acetate), a new cannabinoid marketed for “high” purposes.
While these little-known “high compounds” may have merit, it is the Association’s opinion that these “high compounds” need further study regarding their importation and marketing, and until the benefits and risks of these “high compounds” are known The importation and sale of these “high compounds” for human consumption should be prohibited until the benefits and risks of these “high compounds” are clarified.
However, the possibility that very small amounts of HHC may be present in naturally occurring CBD and Distillate, as well as in stems as building materials, cannot be ruled out, and we believe that separate criteria should be established for these products.
Clearly, the main purpose of the importation and sale of these high compound products is to circumvent the laws regarding THC, which are illegal in Japan.
THC has been studied in detail overseas and the benefits and risks have been defined to a level sufficient to allow countries to change their laws and accept THC for medical and recreational purposes. We are in no way promoting or advocating the legalization of THC in Japan. On the other hand, in light of these high compounds being introduced one after another in such a way as to circumvent the law, we believe that the Japanese government would do well to consider naturally derived THC before flooding the market with these poorly researched synthetic cannabinoid “high compounds”.
MAJIC Position Paper Nr.3
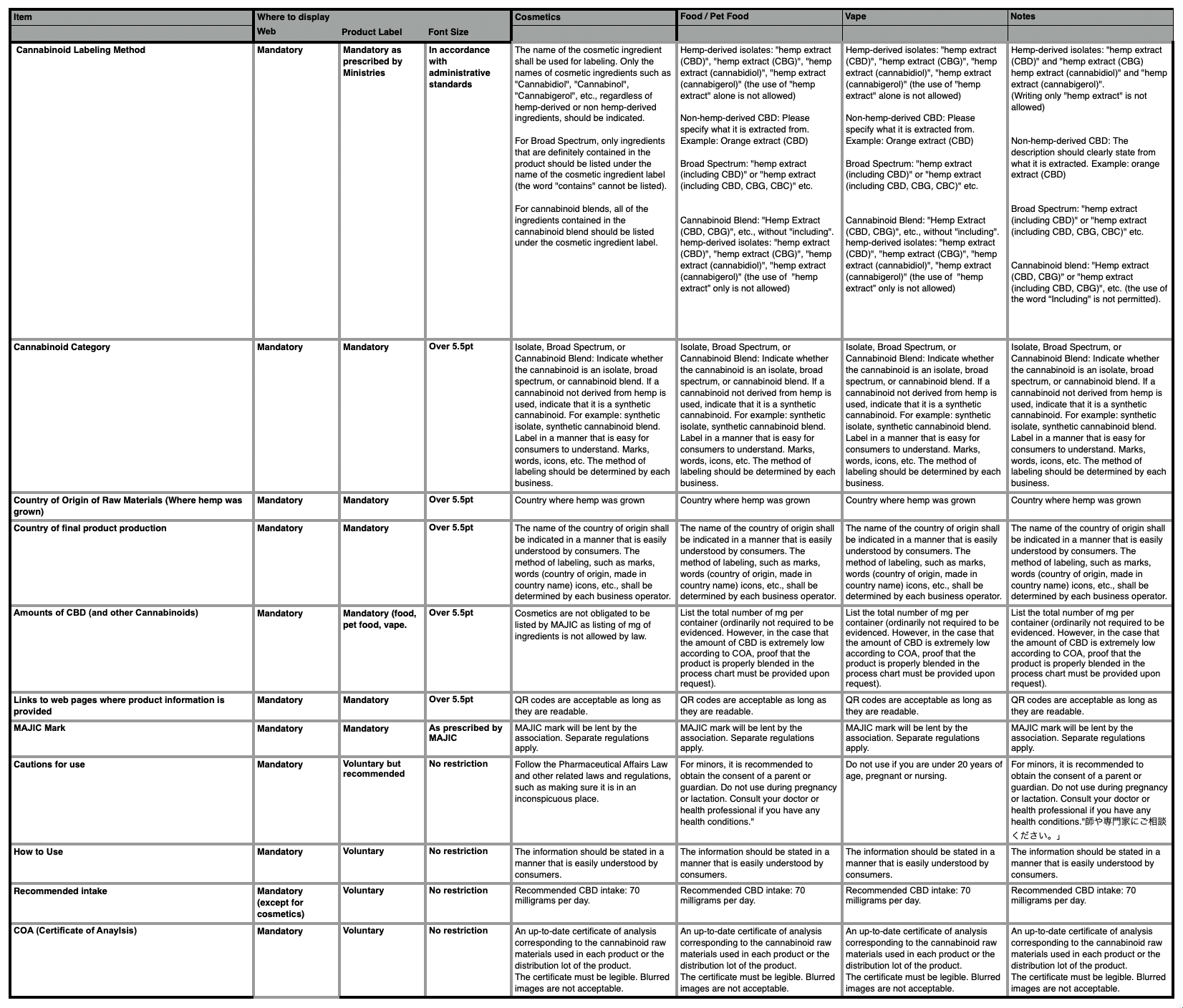
CBD Product Labeling Requirements in Japan
MAJIC guidelines for Japan Cannabis Industry for consumer transparency and trust.
- How to legally and transparently describe cannabinoids contained in a CBD product
- How to describe the type of CBD used in a product (isolate, broad spectrum, blend) and whether the cannabinoids are hemp derived, non- hemp derived or synthetic.
- The country where the hemp was grown,
- The final country where the CBD product was manufactured
- Total number of milligrams of CBD contained in a product
- Link to specific product page containing all information required by MAJIC
- MAJIC Mark (certifying product adheres to MAJIC labeling requirements)
- Cautions for use
- How to Use
- Recommended Daily Intake
- Certificate of analysis for the cannabinoids contained a product.
- Type of Cannabinoid
- The Country where hemp is grown
- The final country where the CBD product was manufactured
- Total number of milligrams of CBD contained in a product
- Link to specific product page containing all information required by MAJIC
- MAJIC Mark (certifying product adheres to MAJIC labeling requirement)
- Cautions for use
- How to use
- How to legally and transparently describe cannabinoids contained in a CBD product
- How to describe the type of CBD used in a product (isolate, broad spectrum, blend) and whether the cannabinoids are hemp derived, non- hemp derived or synthetic.
- The country where the hemp was grown,
- The final country where the CBD product was manufactured
- Total number of milligrams of CBD contained in a product
- Link to specific product page containing all information required by MAJIC
- MAJIC Mark (certifying product adheres to MAJIC labeling requirements)
- Cautions for use
- How to Use
- Recommended Daily Intake
- Certificate of analysis for the cannabinoids contained a product.
MAJIC Position Paper Nr.4
Advocating for the Establishment of THC Levels for the Japanese Cannabis Law Amendment in 2024
Introduction
The regulation of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) levels in hemp and cannabis products is a crucial aspect of contemporary legislative frameworks globally. In the wake of the 2018 Farm Bill in the United States, which established a THC threshold of 0.3% for hemp cultivation, the discussion surrounding appropriate THC levels has gained significant traction. As the Japanese government contemplates its stance on THC regulation, it is imperative to assess the merits of adopting a threshold akin to that set by the US Farm Bill. This position paper aims to advocate for the establishment of THC levels of 0.3% in hemp products in Japan, highlighting the potential benefits in terms of economic growth, public health, and regulatory clarity.
Economic Benefits
Setting THC levels at 0.3% aligns with international standards, facilitating trade and promoting the growth of the hemp industry in Japan. By harmonizing regulations with global norms, Japanese hemp producers gain access to larger markets, both domestically and internationally. This, in turn, fosters economic growth, generates employment opportunities, and stimulates innovation in the hemp sector. Furthermore, increased hemp cultivation can lead to diversification in agricultural practices, providing farmers with alternative revenue streams and contributing to the resilience of rural economies.
Public Health Considerations
Establishing a THC threshold of 0.3% prioritizes consumer safety and well-being. By delineating clear boundaries between hemp and psychoactive cannabis, consumers can make informed decisions regarding product usage. Moreover, stringent regulations ensure that hemp-derived products contain negligible levels of THC, mitigating the risk of accidental intoxication or adverse health effects. Standardizing THC levels enhances product consistency and quality, thereby bolstering consumer confidence and fostering a thriving market for hemp-derived goods, including textiles, food supplements, and cosmetics.
Regulatory Clarity and Enforcement
Clarity in THC regulations simplifies enforcement mechanisms and minimizes ambiguity for law enforcement agencies. By adopting the 0.3% threshold, the Japanese government establishes a clear framework for the cultivation, processing, and distribution of hemp products. This clarity not only facilitates compliance among stakeholders but also streamlines regulatory oversight, reducing administrative burden and enforcement costs. Additionally, well-defined regulations serve as a deterrent against illicit activities, such as the unauthorized cultivation of high-THC cannabis varieties, thereby promoting public safety and regulatory integrity.
Global Trends and Legal Precedents
The establishment of a 0.3% THC threshold mirrors prevailing international trends and legal precedents. Countries around the world, including those within the European Union and North America, have embraced similar regulations, recognizing the therapeutic and economic potential of hemp while prioritizing public health and safety. By aligning with global standards, Japan can leverage best practices, exchange knowledge with international partners, and participate meaningfully in the burgeoning hemp industry on the global stage.
Conclusion
In light of the multifaceted benefits outlined above, we encourage the Japanese government to consider the merits of establishing THC levels of 0.3% for hemp products, in line with the provisions of the 2018 Farm Bill and international standards. Such a measure promises to catalyze economic growth, safeguard public health, enhance regulatory clarity, and align with global trends in hemp regulation. By embracing a forward-thinking approach to THC regulation, Japan can unlock the full potential of its hemp industry while upholding the principles of safety, sustainability, and innovation.
Public Comment Response for THC Levels
MAJIC Advocates for Consumer Safety and the Healthy Growth of the Industry with a 300ppm Δ9-THC Limit for All CBD Products in Japan
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency
Narcotics Control Department
Manufacturers Association for Japan Industrial Cannabis (MAJIC)
Representative Director: Michael Bobrove
Director: Alex Mueller
Director: Kaoru Mfaume
We sincerely appreciate your guidance and support for our industry. As the Manufacturers Association for Japan Industrial Cannabis (MAJIC), an industry organization for manufacturers and sellers of industrial hemp (cannabis) products, we would like to submit our opinions on the amendment of the law and the establishment of regulatory standards as follows.
Regarding the specified ordinance, Item (i) Concentration Standard (Revised Cannabis Control Law Appendix 1, Article 78 Item (b)), we, the Manufacturers Association for Japan Industrial Cannabis, would like to propose that the residual limit value for Δ9-THC in products should be as follows:
For all CBD products: 300ppm (300mg/kg)
No classifications set.
The reasons for this are as follows:
1. The residual limit values for Δ9-THC in final products vary by country, and there are differences in whether classifications are set and how they are set. Some countries do not even have residual limit values for final products. In this context, it is not reasonable for our country to calculate our residual limit values based solely on the intake levels concluded by the European Food Safety Authority as having no adverse effects.
2. Currently, the THC residual values in the product analysis certificates (COA) of products officially imported and distributed are non-detectable (below the limit of detection (LOD) or limit of quantification (LOQ), or both). The LOD and LOQ values vary by testing agency, and based on past performance, it is industry consensus that below 300ppm is a reasonable guideline. Furthermore, there have been no issues with THC in COA-certified products, and safety is considered to be ensured. Considering the industry’s scale and market maintenance and development, we believe that continuing with the conventional guideline limit (300ppm) is acceptable.
3. The standard of 300ppm for residual limit value is lower than the values concluded by WHO and other public and testing agencies as having no impact on health (including intoxication).
4. With the current technology and facilities of cannabis cultivators in our country, it is impossible to produce CBD products with a residual limit value of less than 1ppm from cannabis plants that meet the standard (0.3% as prescribed by ordinance). This poses a challenge in terms of the limited applications of the products and hinders the resolution of the issue of decreasing numbers of cannabis cultivators.
From the above, we believe that setting excessively strict standards that do not align with conventional and current practices poses a danger of market destruction and increases the risk of non-compliant products circulating despite penalties. Based on our knowledge and verification accumulated since the early days of the CBD market, we propose that the optimal residual limit value should be 300ppm.
On the other hand, we strongly support the establishment of penalties and strict regulations. There have been instances of violations we do not desire due to the characteristics of cannabis-derived products, which are a significant impediment to the normal expansion and development of our industry. We hope that establishing regulations will create an ethical and transparent market.
The Manufacturers Association for Japan Industrial Cannabis (MAJIC) is the first industry organization in Japan for manufacturers and sellers of industrial hemp (cannabis) products manufactured and sold in compliance with Japanese laws and regulations. We were established by industry leaders who recognized the necessity of ethically leading and growing the business related to legal cannabis products in Japan, and we are engaged in various activities with a sense of mission.
Ensuring Fair Standards for THC Testing and Cannabis-Derived Products in Japan
As the regulation of cannabis-derived products in Japan tightens, particularly regarding the limit of detection (LOD) for THC, MAJIC (Manufacturers Association for Japan Industrial Cannabis) expresses deep concerns about the potential negative impacts on the cannabis industry. Discrepancies in testing methods, stringent regulatory standards, and a lack of clear guidelines are causing significant operational challenges. This position paper highlights these issues and proposes solutions to promote a balanced, fair, and internationally consistent regulatory framework. Our goal is to support the growth and innovation of the industry while ensuring public safety.
Concerns and Proposed Measures
1. Variability in Test Results
Concern:
There is inconsistency in THC concentration results depending on the testing institution and timing. CBD products (including CBN, CBG) that were certified as containing less than 1 ppm of THC before importation sometimes show higher levels of THC when retested in Japan or overseas, with unknown causes. The reverse also occurs. In the case of CBN, foreign producers have stated that maintaining THC levels below 10 ppm is almost impossible, and even if 10 ppm can be achieved at one stage, the next processing stage often results in higher concentrations, confirming a wide range of variability. This variation poses a significant risk of non-compliance despite efforts by companies to meet Japan’s stringent regulatory requirements.
Measures:
- Allow reasonable THC variability. We recommend introducing a permissible range for natural variations in THC levels based on testing conditions, reflecting manufacturing realities while maintaining safety standards. This approach aligns with other regions in the international market.
- Propose the establishment of unified testing procedures and detection standards.
2. Strict Residue Limit Standards in Japan
Concern:
The Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare in Japan has proposed strict LOD standards for THC: 10 ppm for oils and 1 ppm for other products. These are among the most stringent globally. In practice, even with unified testing procedures and detection standards, it cannot be denied that results and THC variability exceeding 10 ppm could occur, making it unrealistic to clear this standard. Meeting these standards is particularly challenging for CBN-containing products, which could result in the inability to distribute all cannabis products in the market.
Measures:
Propose the establishment of reasonable residue limit standards and unified testing procedures and detection standards.
3. Lack of Unified Testing Procedures and Detection Standards
Concern:
The use of different methods and equipment by different institutions leads to inconsistent test results for the same product. This lack of standardization creates uncertainty for companies and increases the risk of compliance failure.
Measures:
MAJIC urges the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare to establish unified testing procedures and detection standards applicable to all testing institutions, both domestic and international. These should be developed in cooperation with internationally recognized, authoritative testing bodies.
4. Uncertainty Regarding Authoritative Test Results
Concern:
There are no guidelines on which test results are legally valid in the event of discrepancies between test results before and after importation or distribution. Moreover, the process for handling products that pass foreign testing but exceed Japanese THC standards upon retesting is unclear, leaving companies facing regulatory uncertainty.
Measures:
- Accreditation of Testing Institutions: We propose that the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare designate both domestic and foreign public testing institutions as well as certified testing institutions. Establishing criteria for accreditation would not only reduce the risk of inconsistencies between pre- and post-import test results but also increase trust in test results, providing companies with clear compliance procedures.
- Clear Guidelines for Authoritative Test Results: It is essential to provide clear guidelines on which test results are authoritative. In cases of discrepancies, a transparent dispute resolution process involving third-party arbitrators should be established to resolve issues fairly and swiftly.
5. Reducing the Burden on Companies and Applying Transitional Measures
Concern:
The retroactive application of the new system places an excessive burden on companies, requiring them to voluntarily recall non-compliant products, leading to significant market disruption and operational difficulties.
Measures:
- Application of Transitional Measures: We strongly request the introduction and application of transitional measures that allow products imported, manufactured, processed, or distributed before the implementation of the new system to comply with the previous standards after the system change.
- Alleviation of the Burden on Companies Caused by the Transition to the New System: The current legal revisions and the new system impose an unprecedented burden on companies. We hope that financial support will be provided in the form of government subsidies or tax incentives to alleviate the financial burden of voluntary product recalls and adaptation to new regulations. This support will help companies comply with the new system and maintain stable operations.
Conclusion
MAJIC commits to working closely with regulators, testing institutions, and industry stakeholders to ensure the continued growth of Japan’s cannabis industry while adhering to public safety standards. By addressing test result variability, establishing clear guidelines, and providing transition and financial support, a regulatory framework that balances innovation and compliance can be built. We urge the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare to collaborate with other organizations and industry stakeholders to carefully review regulations and establish a working group to ensure a fair, transparent, and sustainable market environment. Together, we can build a regulatory system that fosters public trust and industry growth.
Position Paper No. 7
On CBN (Cannabinol): Promoting Responsible Use in Japan and Industry-Led Voluntary Governance
Introduction
CBN (Cannabinol) is a minor cannabinoid derived from hemp and is increasingly used in Japan as a food or supplement. It is mainly used for relaxation and sleep support. As the regulatory environment in Japan evolves, MAJIC (Japan Association of the Cannabis Industry) aims to promote responsible self-regulation within the industry to ensure safety, encourage responsible innovation, and avoid excessive regulatory tightening.
1. Recommended Intake Guidelines
- MAJIC recommends starting with a CBN intake of 5–20mg per dose.
- The maximum recommended daily intake is set at 60–100mg.
- This is based on current usage trends, early scientific knowledge, and the precautionary principle.
2. Product Labeling and Transparency
All CBN products must comply with MAJIC’s “Cannabinoid Product Labeling Guidelines (Revised December 2024).” https://majic.jp/ja/news/12-12-cbd-label-guideline/
The specified labeling items are as follows:
・How cannabinoids are displayed
・Types of cannabinoids
・Hemp origin
・Country of origin
・CBD content*
・Link to a webpage with product information
・MAJIC mark
・Precautions for use
・Usage instructions
・COA (Certificate of Analysis)
*CBN should be labeled in the same manner as CBD.
3. Warnings and Notices
Additionally, for CBN, it is strongly recommended to include the following warnings on the product and on the web pages providing product information:
・If you have any medical conditions, please consult your doctor before use.
・Do not consume if you are driving or operating machinery.
・Avoid excessive intake; start with a small amount and observe how you feel.
4. Product Design for Proper Dosage Management
- Recommend product forms that allow easy dosage control (e.g., gummies, breakable chocolate, individually packaged items).
- Design products so that a single dose does not exceed the recommended daily amount.
5. Responsibility in Sales
- MAJIC emphasizes responsibility in sales behavior rather than restricting sales locations.
- Sales methods and marketing should follow the same moderate standards as other legal active ingredients such as caffeine.
6. Marketing and Advertising Guidelines
- Under current Japanese law, expressions suggesting treatment or prevention effects or medical claims are prohibited.
- Avoid expressions that evoke intoxication, dependence, or abuse.
7. Supply Chain and Traceability
- Ensure traceability of each lot from raw materials to final product.
- COAs (Certificates of Analysis) should include verification of non-detectable levels of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), and test results for heavy metals, residual solvents, and microbes.
8. MAJIC’s Basic Policy and Future Initiatives
MAJIC will continue to contribute to consumer safety, advancement of scientific knowledge, and sustainable market development. While valuing constructive dialogue within the industry, we will promote practical, ethical, and cautious cannabinoid innovation in compliance with Japanese legal and consumer protection frameworks. This position paper is expected to evolve and improve through continued discussions among MAJIC members as scientific understanding and regulations progress.